Objective: To reveal the effect of preoperative Kegel exercises on early period continence rates
after open radical prostatectomy.
Materials and Methods: Data of patients with open radical prostatectomy between January
2019 and July 2022, in a tertiary academic health center were retrospectively reviewed. Patient"
characteristics, perioperative parameters and postoperative follow-up results were recorded.
Patients were divided into two groups as those who did Kegel exercises in the preoperative
period and those who did not, and groups were compared.
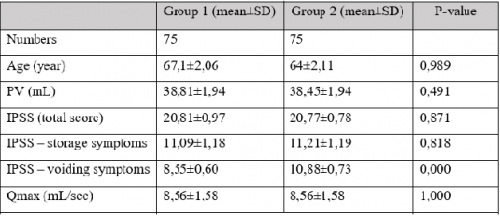
Results: There were 38 patients in the Kegel exercise group and 40 patients in the other group.
Postoperative 1st month and postoperative 3rd month incontinence rates were similar between
the groups (p=0.406, and p=0.387). At 6th months postoperatively, the rate of incontinence in
the Kegel group was 7.9%, while it was 25.0% in the other group (p=0.043). Similarly, the rate
of incontinence at 1st year postoperatively was significantly lower in the Kegel group (5.3% vs
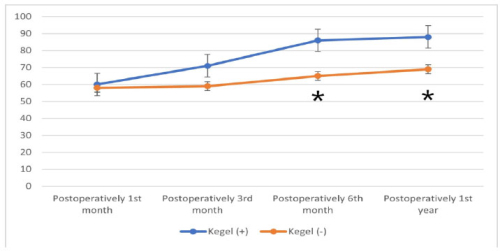
20.0%, p=0.001). At 6 months postoperatively, the QoL score in the Kegel positive group was
86, while it was 65 in the other group (p=0.001). In the postoperative 1st year controls, the
quality of life (QoL) score was statistically significantly higher in patients with preoperative
Kegel exercise (p=0.001).
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated that preoperative Kegel exercises had a significant
positive effect on continence rate after radical prostatectomy in the postoperative 6th month and
in the first year follow-up, and preparative Kegel exercises were significantly associated with
higher quality of life scores at 6th months and 1st year follow-up.