Objective: To evaluate the clinical, anatomical, and stone-related factors in patients who
underwent shock wave lithotripsy (SWL) for proximal ureteral stones and to identify the risk
factors associated with the subsequent need for urgent ureteroscopy (URS).
Materials and Methods: Patients who underwent SWL for proximal ureteral stones were included
in the study. Demographic and clinical characteristics, including age, body mass index (BMI),
serum creatinine, white blood cell count, hemoglobin, and platelet count, were recorded. Stone
characteristics and anatomic factors were determined using parameters obtained from non-contrast
lower upper abdomen computed tomography scans: stone density (HU), stone diameter, renal
pelvis urine density (HU), perirenal stranding, stone-skin distance, and ureteral wall thickness.
Patients who underwent emergency URS were grouped. Logistic regression analysis was used to
identify risk factors predicting the need for urgent URS in patients.
Results: Among the study population, 232 patients (83.8%) did not require urgent URS (Group 1),
while urgent intervention was necessary in 45 patients (16.2%) (Group 2). Patients in the urgent
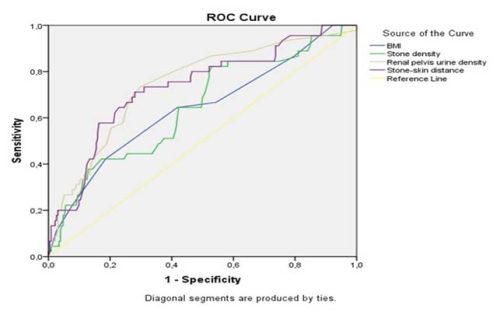
URS group demonstrated a significantly higher body mass index (26 [24-27] vs. 25 [24-26] kg/m²,
p = 0.002). Non-contrast CT findings revealed that renal pelvis urine density and stone–skin
distance were markedly greater in the URS group (13 [9-36] vs. 8 [6-11] HU, p < 0.001 and 12 [6-
16] vs. 9 [7-13] cm, p < 0.001, respectively). Stone density was also higher among patients
requiring URS (862 [784-1014] vs. 786 [665-956] HU, p = 0.002). In multivariable analysis, BMI
(OR 1.245, 95% CI 1.025–1.512, p = 0.028), stone density (OR 1.003, 95% CI 1.001–1.004, p =
0.002), renal pelvis urine density (OR 1.032, 95% CI 1.009–1.055, p = 0.006), and stone–skin
distance (OR 1.654, 95% CI 0.986–1.846, p = 0.004) remained as independent predictors.
Conclusion: BMI, stone density, renal pelvic urine density, and stone–skin distance parameters
may serve as useful guidance when considering SWL for patients with proximal ureteral stones.
Prospective studies with larger samples are needed to support the findings.