Assoc. Prof. Ekrem GUNER, MD

Dear colleagues,
I am honored to share with you the second issue of 2025 (volume 5, issue 3) of the Grand Journal of Urology (Grand J
Urol) with the contributions of many respected researchers and authors.
Grand Journal of Urology (GJU) aims to carry written and visualscientific urology studies to academic platforms and to
make significant contributions to the science of urology. Our journal has been abstracted/indexed in Tubitak Ulakbim TR
Index, EBSCOhost, J-Gate, SciLit, ResearchGate and Google Scholar international databases. As of these achievements,
the Grand Journal of Urology (GJU) has taken its place among the journals indexed by national and international databases.
In this issue of our journal, there are many valuable articles under the subheadings of Andrology, Endourology, Functuional
Urology, Pediatric Urology, Urolithiasis and Urologic Oncology. I hope that these carefully prepared articles will make
important contributions to valuable readers, researchers and the urology literature.
On this occasion, I would like to express my heartfelt gratitude to our authors who have contributed to our journal with
their articles, to our reviewers who have meticulously evaluate the articles.
Respectfully yours
September 2025
Assoc. Prof. Ekrem GUNER, MD
Editor-in-Chief
Muzaffer Tansel Kılınç, Ali Sezer, Mehmet Serkan Özkent, et al.
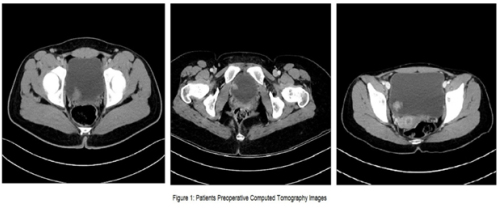
Urothelial papillary neoplasms of the bladder in children and
adolescents are rare and differ from adult papillary neoplasms
in terms of clinical, histological, and pathological outcomes
and prognoses [,]. While 0.4% of urothelial carcinomas (UC)
are observed in patients under 20 years of age, only 0.03% are
witnessed in patients under 16 years of age [].
The most common symptom at the time of diagnosis is
hematuria. Dysuria, suprapubic pain, frequency, and obstructive
symptoms are other less common symptoms []. Bladder
tumors in the pediatric population are commonly detected by
urinary system ultrasound (USG) [,]. A cystoscopy should be
performed under general anesthesia for definitive diagnosis and
treatment if a bladder tumor is suspected due to the patient's
medical history and radiological imaging [].
Urothelial carcinomas usually tend to be low grade and
present a lower incidence of invasiveness in children and
adolescents [,]. According to a World Health Organization
(WHO) classification in 2004, approximately 3% of pediatric
cases are high-grade diseases, while most cases are papillary
urothelial neoplasms of low malignant potential (PUNLMP)
[,]. Therefore, the incidence and recurrence rates of invasive
tumors diverge from those of adults. There is also a higher
disease-free survival rate in pediatric cases [,,]. The
recurrence rate ranges from 8% to 15%, and more than twothirds
of recurrences occur in the first year [,,,].
Urothelial carcinomas are rare in the pediatric population,
so standardized recommendations have not been clearly defined
for their management. Although some authors state that the adult
follow-up protocol may be preferred, uncertainty remains in the
management of pediatric bladder UC, which differs significantly
from adults in terms of clinical, histological, and prognosis [,].
In this study, we report our experience and long-term followup
data with low-grade urothelial bladder neoplasms in pediatric
patients.
Metin Savun, Fatih Yanaral, Ufuk Çağlar, et al.
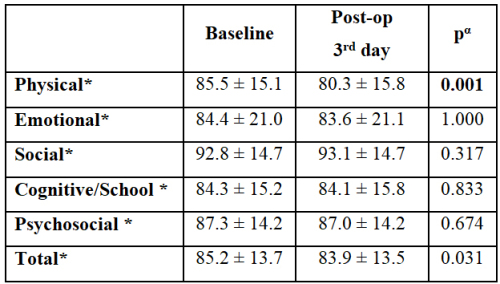
Urinary system stone disease; is a common health problem
prevalence ranging from 1-20%. The prevalence of urolithiasis
is increasing and children are more likely to experience
recurrence [,]. Although endourological treatments are
becoming widespread with the miniaturization of endoscopic
instruments, extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (SWL) is
widely used in the treatment of pediatric urinary stone disease.
SWL is a noninvasive, effective and reliable method []. It is
easier for children to reduce shock wave transmission due to
the smaller body volume, shorter ureter length and high ureter
compliance facilitating spontaneous disposal of stone fragments
[]. According to the European Urology Association; SWL is the
first-choice method in children with renal and ureteral stones up
to 20 millimeters [].
In pediatric patients with urinary stone disease, the stonefree
rate of SWL has been reported as 67-93% in the short term
and 57-92% in long-term follow-up studies []. However, the
complication rates of SWL are very low []. Pediatric SWL
is a painful procedure. It is often performed under sedation or
general anesthesia to reduce pain and ensure patient immobility.
Both the SWL procedure itself and the anesthesia administered
may affect the quality of life (QoL) of the child. Although there
are many studies on the efficacy and safety of pediatric SWL, to
the best of our knowledge, no published studies have explored
the association between SWL and QoL in pediatric patients.
Assessing QoL in children is critical, as it impacts their
physical, emotional, and social development, as well as family
dynamics. In this study, we aimed to determine the relationship
between pediatric SWL and patients" QoL using a validated QoL
scale.
Kenan Yalçın, Engin Kölükçü
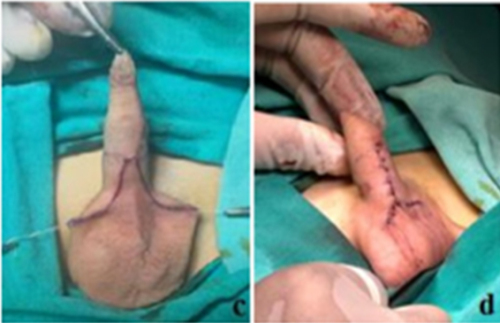
Webbed penis is a congenital anomaly in which a fold of
skin extends from the scrotum to the ventral surface of the penile
shaft, obscuring the penoscrotal angle []. It is most commonly
identified during infancy or at the time of circumcision. This
condition may result in a visually shortened penis and is
recognized as a frequent cause for delayed circumcision [].
Performing circumcision without correcting the web can lead to
downward urine flow during childhood and may impair sexual
function in adulthood. Therefore, surgical correction of the web
is generally considered mandatory prior to circumcision [].
However, correcting the web post-circumcision is often more
challenging due to the loss of preputial tissue.
In Turkey, circumcision is a nearly universal practice
performed for cultural and religious reasons. In some cases, it
is carried out by non-specialist practitioners, which may lead
to underdiagnosis of such anomalies [,]. Numerous studies
have investigated the surgical correction of primary webbed
penis [,-]. The main goal of treating penoscrotal webbing is
to elongate the ventral penile skin by transecting the web. This
is traditionally achieved using a transverse incision followed
by vertical closure—commonly referred to as the Heineke-
Mikulicz technique []. Other surgical methods have also been
introduced, including V-Y plasty, Z-plasty, lateral parapenile
incisions, and preputial flap rotation [].
The present study aims to compare the clinical outcomes
of Heineke-Mikulicz and V-Y scrotoplasty techniques in the
surgical correction of penoscrotal webbing in pediatric patients
with varying grades of severity.
Yunus Çolakoğlu, Ali Emre Fakir, Ali Ayten, et al.
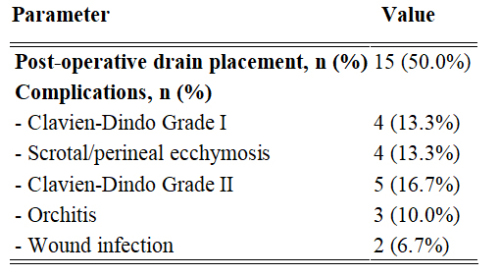
Penile prosthesis implantation (PPI) is a highly effective
treatment for men with erectile dysfunction (ED) who fail
first- and second-line therapies []. The modern inflatable
penile prosthesis (IPP) era began in 1973 when Brantley Scott
reported implanting silicone bodies, a reservoir, and a control
pump in five patients []. Early IPPs, while effective for organic
ED, had mechanical failure rates up to 50% within five years
[]. Prosthesis infection, a severe complication in andrological
surgery, increases morbidity and healthcare costs, exceeding
initial implant costs by over six times []. Infection rates range
from 2% for primary implantations to 18% for replacements [].
Despite high patient satisfaction with IPPs, issues
like discomfort, inadequate inflation, deformity, palpable
abnormalities, or painful intercourse may require revision
surgery []. Revision surgery effectively addresses infections,
mechanical failures, or patient dissatisfaction, with most
patients satisfied post-revision []. Most patients undergoing IPP
replacement report satisfaction and need no further intervention
[]. However, revision surgery carries higher risks of infection
and complications than primary surgery [], posing challenges
for patients, surgeons, and healthcare systems []. This study
evaluates the feasibility and safety of PPI revision surgery.
Duygu Kurtuluş, Selma Dağcı, Ferhat Yakup Suçeken, et al.
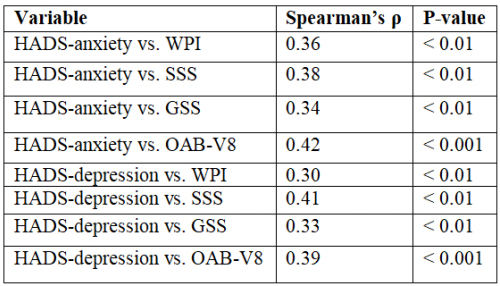
Fibromyalgia (FM) is a chronic, centralized pain disorder
characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue,
cognitive dysfunction, and a variety of somatic symptoms.
Beyond its hallmark pain features, FM frequently presents
with genitourinary complaints, including lower urinary tract
symptoms (LUTS) such as urinary urgency, frequency, and
nocturia. Among these, overactive bladder (OAB) has gained
attention as a functionally significant and underrecognized
component of the FM symptom complex [,].
The pathophysiology of FM and OAB is believed to share
common mechanisms, most notably central sensitization-a state
of amplified neural signaling in the central nervous system
that leads to heightened pain and sensory perception [,]. In
both disorders, dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system,
altered pain processing, and neurogenic inflammation have been
implicated. These shared neurobiological pathways suggest
that OAB in FM may not merely be coincidental but rather a
manifestation of overlapping central dysfunction [,,].
In parallel, psychiatric comorbidities-particularly anxiety
and depression-are prevalent in both FM and OAB populations.
Up to 60–70% of FM patients experience clinically significant
symptoms of depression or anxiety, which have been shown
to exacerbate pain, fatigue, and somatic burden []. Similarly,
psychological distress has been associated with increased
urinary urgency and incontinence episodes in patients with OAB,
potentially through heightened arousal, cortical hypervigilance,
and altered bladder perception [,].
Although the independent associations of psychiatric
symptoms with FM and OAB are well documented [,]
limited data exist regarding their combined burden in patients
experiencing both conditions [,]. In particular, the
impact of psychiatric comorbidity on symptom severity and
functional status in FM patients with OAB remains poorly
understood [,]. Elucidating this relationship may inform the
development of more integrative treatment strategies [,].
The present study aimed to investigate the prevalence and
clinical significance of anxiety and depression in FM patients
diagnosed with OAB, using validated screening instruments.
We further evaluated the relationship between psychiatric
symptom burden and FM/OAB severity to better understand the
interplay between psychological distress and visceral-somatic
sensitization in this patient population.
Savaş Özgür Ağlamış, Selver Kübra Akkaya, Ahmet Asfuroğlu
Two major earthquakes with moment magnitudes of 7.8 and
7.5 struck the southern and eastern Türkiye on 6 February 2023,
directly and indirectly affecting 15 million people and causing
more than 50000 lives []. The earthquakes were followed by at
least 11,000 aftershocks with moment magnitudes up to 6.7. The
earthquakes of 6 February 2023 were recorded as the earthquakes
with the highest number of casualties throughout the history of
the Republic of Turkey []. After the earthquake, survivors were
faced with a lack of food, thirst, cold weather conditions, health
problems, and shelter problems for a long time.
The most common problems faced after natural disasters
such as earthquakes are sexual disorders and fertility health
[]. The extent of contraceptive methods, sexual violence, and
the prevalence of sexually transmitted diseases are among the
main consequences of earthquakes for sexual and reproductive
health []. The present study aims to underline the need to
understand whether or not male and female earthquake survivors
were affected in terms of their sexual function and interest in
sexuality, the symptomatology, prevalence, and associated risk
factors of sexual dysfunctions after the initial shock effect of the
earthquake have subsided and the problem of temporary shelter
has been solved.
Hüseyin Aytaç Ateş, Muhammet Hilmi Enes Aracı, Yusuf Şahin, et al.
Urolithiasis is one of the most common conditions
encountered in urological practice, with its prevalence ranging
from 1% to 20%, depending on geographical, ethnic, dietary, and
genetic factors []. The high frequency of both newly diagnosed
and recurrent stone disease causes a significant psychosocial
and economic burden on patients, healthcare providers, and the
healthcare system, which cannot be overlooked []. Untreated
urinary tract stone disease significantly increases the risk of
acute and chronic renal failure, urinary tract infections, and other
complications associated with stones. A considerable number of
these stones necessitate active intervention [,].
Surgical treatment options include ureteroscopy (URS),
shock wave lithotripsy (SWL) and percutaneous nephrolithotomy
(PCNL) for most of the patients. It is known that among these
treatment options, URS has lower complication rates compared
to PCNL and higher stone-free rates compared to SWL []. With
technological advancements and the development of endoscopic
devices in more practical forms, ureteroscopy has gained
increasing application even in >2 cm diameter stones. Due to
its high treatment success and low morbidity, it is becoming an
increasingly preferred treatment option for the management of
ureteral and kidney stones [].
Although a substantial proportion of complications following
URS are minor and do not require further intervention, the
overall complication rate can reach up to 25% [,]. Among
these, infectious complications such as postoperative fever,
urinary tract infections, systemic inflammatory response
syndrome (SIRS), and urosepsis are particularly concerning
[-]. Preoperative bacteriuria is a known risk factor for
such complications, especially in patients with additional
risk factors including female gender, chronic diseases, higher
American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) physical status
classification system score, hydronephrosis, or infectious stones
[,]. While prophylactic antibiotics and careful perioperative
management can help reduce these risks [] a positive
preoperative urine culture remains a significant predictor of
postoperative infection and should be managed accordingly
[]. However, in patients with urinary tract stone disease,
achieving sterile urine cultures may not always be possible due
to persistent or recurrent bacteriuria and contamination [].
The belief that persistent urine culture positivity increases the
risk of surgical complications may heighten anxiety for both the
patient and the urologist. This concern often leads to repeated
antibiotic use, which contributes to bacterial resistance and may
increase patient's morbidity []. Additionally, delaying surgery
in pursuit of urine sterilization prolongs hospitalization, raises
healthcare costs, and may result in irreversible renal damage due
to ongoing obstruction []. Despite these challenges, there is
currently no clear consensus on whether URS should be delayed
until urine cultures are sterile or whether it can be performed
safely under targeted antibiotic therapy [].
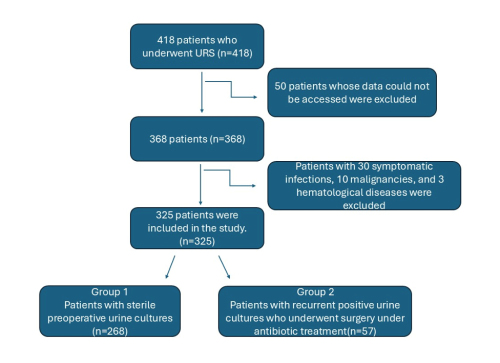
In this single-center, retrospective study, we hypothesized that
URS can be performed safely in patients with persistent positive or
contaminated urine cultures, provided that appropriate antibiotic
treatment is administered. Therefore, we aimed to compare the
surgical outcomes of patients with sterile preoperative urine
cultures and those with persistent non-sterile cultures.
Vinay Nagendra Kaushik, Gopalkrishna Sp, Srikanth Kulkarni
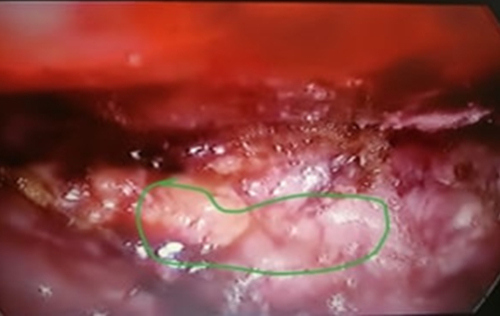
Malakoplakia, derived from the Greek term for "soft
plaque", [] is a rare chronic inflammatory disease first
identified by Professor von Hansemann in 1901 and reported
by Michaelis and Guttman in 1902. Although benign, it
frequently resembles malignant carcinomas due to its tumorlike
mass formations, complicating its diagnosis. Depending
on the location, the disease typically manifests as raised, grey
lesions of varying sizes or soft, yellow mucosal plaques during
physical examination [].
Though malakoplakia can affect multiple organs, it
primarily targets the urinary system, especially the bladder,
with less frequent involvement of the kidneys and ureters [].
Malakoplakia in the urinary system can lead to acute kidney
injury, frequent urinary tract infections (UTIs), and renal
failure, but is rarely fatal [].
The symptoms vary depending on the affected organ: in
cases involving the urinary tract and/or bladder, patients may
experience frequent urination, urinary urgency accompanied
by vague discomfort, hematuria, and bladder irritability; in
instances of renal and ureteral involvement, symptoms can
include lower back pain and fever [,].
The exact cause of bladder malakoplakia is poorly understood,
but its pathogenesis is based on three primary hypotheses. The
first hypothesis suggests bacterial infections, particularly those
caused by E. coli, often occuring after a prolonged and recurrent
history of chronic UTIs. The bladder's local environment
fosters bacterial proliferation and triggers an inflammatory
reaction in the bladder lining []. The second hypothesis points
to immunocompromised states or long-term chronic conditions
such as HIV, tuberculosis, sarcoma, diabetes, lymphoma, and
ulcerative colitis []. Third, it is believed to stem from an acquired
defect in the bactericidal function of macrophages. Normal
microtubular function and phagolysosomal activity require betaglucuronidase
and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP).
Reduced levels of these enzymes result in impaired clearance of
pathogenic organisms due to the persistence of phagolysosomes.
The characteristic Michaelis-Gutman bodies, which are calcified
intracytoplasmic inclusions, represent the phagolysosomes that
have failed to undergo exocytosis [,,].
Malakoplakia in the genitourinary system typically shows
a higher prevalence in females, with a female-to-male ratio
of 4:1. The age of diagnosis can range from six weeks to 85
years, with the average age at which individuals start showing
symptoms being 50 years [,].
Ender Cem Bulut, Mahmut Uğurlu, Mustafa Kaba
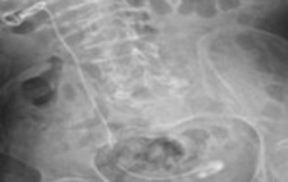
Double-J (DJ) stents are essential tools in various urological
procedures []. With the increasing frequency of DJ stent use,
stent-related morbidities have become more prevalent. In the
short term, complications such as pain, irritation, infection, and
hematuria may occur. In the long term, serious complications
including encrustation, urolithiasis, stent migration, fracture,
renal damage, and even death have been reported []. DJ
stents may require removal through extracorporeal shock
wave lithotripsy (ESWL), cystolithotripsy, laser lithotripsy,
percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PNL), open surgery, or
combinations of these approaches [].
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a neurological disorder affecting
motor function and is frequently associated with urological
complications, particularly lower urinary tract dysfunction [].
The management of urolithiasis in patients with CP is often
challenging due to physical disabilities, anatomical variations,
and accompanying comorbidities [].
Fractured DJ stents are rare clinical occurrences. In this case
report, we present the endourological management and singlesession
removal of a severely encrusted DJ stent that remained
in situ for approximately 2.5 years.